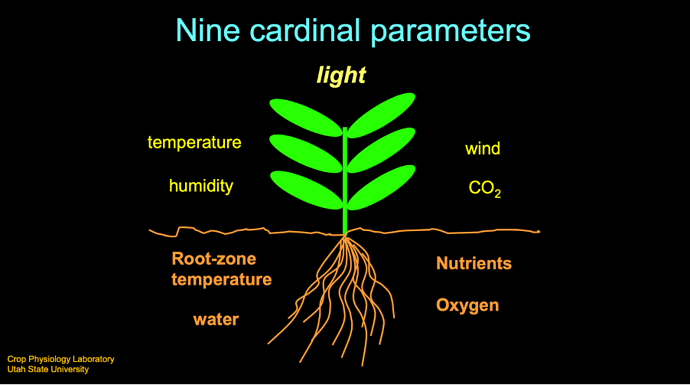
The vital needs of a plant are very much like our own - light, water, air, nutrients, and a proper
temperature. The relative importance of each of these needs differs widely among plants. The ability
of a plant species to spread throughout a geographic area is a direct result of its adaption to the abiotic
and biotic components of the area. Although most habitat components act on a plant simultaneously
and should be considered together, the lack of one essential component can determine the health of a
plant. This factor, whatever it may be, is referred to as a limiting factor. The concept of limiting factors
applies to all aspects of a plant’s interaction with its habitat.
Water is crucial to all life. Even the most hardy desert plants need water to grow. There are three potential situations with water: too much, too little and, of course, just enough. If a plant’s soil has too much water, the roots can rot, and the plant can’t get enough oxygen from the soil. If there is not enough water for a plant, the nutrients it needs cannot travel through the plant. A plant cannot grow if it doesn’t have healthy roots, so the proper balance of water is key when growing plants. There are a few simple things you can do to check the amount of water in the soil and ensure that there is the correct entry of water in a plant. One of the quickest ways is to just put your finger in the soil, up to your knuckle. If the soil is moist, it has enough water; if it is dry, you need to water the plant. If the pot feels lighter than usual, or if the soil is pulling away from the sides of the pot, it needs more water and may even be in need of rehydration. How Does Water Help a Plant? How does water help a plant? What does water do for a plant? Water helps a plant by transporting important nutrients through the plant. Nutrients are drawn from the soil and used by the plant. Without enough water in the cells, the plant will droop, so water helps a plant to stand upright. Water carries dissolved sugar and other nutrients through the plant. So, without the proper balance of water, the plant not only is malnourished, but it is also physically weak and cannot support its own weight. How does water travel up a plant? The water a plant needs enters through the root system. The water then travels up a plant through the stem and into the leaves, flowers or fruit. The water travels up a plant through its xylem vessels, which are like capillaries that move the water into the different parts of the plant. What does water do for a plant in other ways? It helps the plant maintain the proper temperature as water evaporates. When moisture evaporates from the surface area, the plant draws more water up through the roots to replace what was lost, traveling through the plant’s circulatory system. Knowing how water affects plant growth and what water does for a plant, it’s easy to remember that keeping your plant properly watered is important to its health and looks.
Light reaching the surface of a plant is either absorbed, reflected, or transmitted. Energy, in the
form of sunlight is one of cess by which green plants manufacture food, mainly sugars, from carbon
dioxide and water in the presence of chlorophyll (a green pigment), utilizing light energy and releasing
oxygen and water. Together the quality, quantity, and duration of light influences plant growth. Plants
grown in direct sunlight are typically compact, where as those in shade are taller and elongated. Seeds
may start to grow (germinate) without light, but the plant growing from it must have light if it is to
continue to grow.
Water is essential for life, it is one of the most important requirements for plant growth. Water
is the main component in plants cells, it keeps the plant turgid (stiff), it is used in photosynthesis, and
transports nutrients throughout the plant. Plants also use water to lower leaf temperature, increase
mineral absorption, and pull water from the roots to the top of the plants through a process known as
transpiration.
One of the raw materials used in photosynthesis is carbon dioxide. The content of carbon dioxide
in the atmosphere is relatively stable at about 0.03 percent, a seemingly small amount but totaling
roughly 2,000,000,000,000 tons in the atmosphere surrounding the earth. Carbon dioxide is continually
being added to the air by respiration of plants and animals, decaying organic materials, combustion of
fuels, and volcanic activity. Carbon dioxide diffuses through the stomata (pores or openings in a plants
epidermis) from the atmosphere into the intercellular spaces of the leaf.
Wind is air in motion and can be both beneficial and harmful to plants.
Wind can benefit plants. The hormone ethylene is widely considered to help cause aging or maturity in a plant due to its role in accelerating such developmental processes as ripening, senescence, and abscission (the process where the plant loses its leaves or fruit). Ethylene also regulates many aspects of growth and development throughout the plant’s entire life cycle. Water respiration - WIND = WATER UPTAKE IN STEMS
by accelerating the transfer of heat from leaf surfaces and increasing circulation in areas prone to fungal
growth. Wind can be detrimental to plants by causing excessive drying, and
sometimes destroying plants.
In addition to carbon dioxide and water, plants need 17 different nutrients to maintain growth.
Although carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen are obtained from the air, most nutrients that a plant needs
must be present in the soil or growing medium. These elements are divided into macro and micro
elements. Macro nutrients needed in the largest amounts are nitrogen (N) for healthy foliage,
phosphorus (P) for flower development, and potassium (K) for root growth.
The soils in which plants grow consists of a mixture of mineral materials, organic matter, water,
and air in varying proportions. The small fragments of mineral materials are derived from rock over
long periods of weathering. The organic matter consists of living organisms, their excretions, and decay
products. The texture of soils refers to the sizes of the particles that dominate. The texture of a soil
influences the amount of air, water and nutrients held in the soil. In general, the penetration of air,
water, and roots occurs much more readily through soils in which large particles (sand) dominate. On
the other hand, water-holding capacity and fertility are mainly a result of small particle size (silt and
clay) and organic matter.
The root zone temperature is a crucial factor for the healthy growth of the plant. Root temperature can improve several parameters throughout the plant growth cycle. For instance, optimal temperature can help with biological activity, with mineral and water uptake, with fighting pathogens and roots diseases. Therefore, plants grow healthier quicker. The changes in the root temperature can affect the yield both in terms of quantity and quality.
One of the issues that cause damage to the plants is the low oxygen percentage around the root zone. When you have high or low temperature fluctuations between day and night, the oxygen levels in the root zone is directly affected. Through optimal and stable range temperature, you can provide a higher percentage of oxygen to the roots and ensure optimal biological activities.